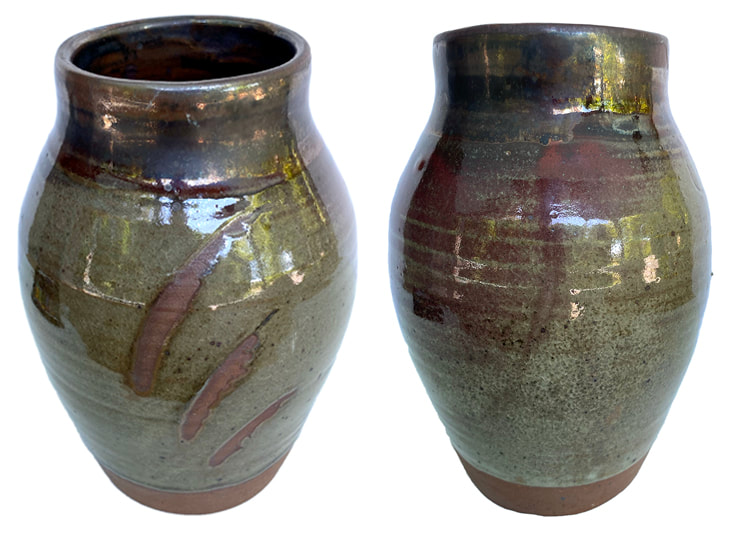
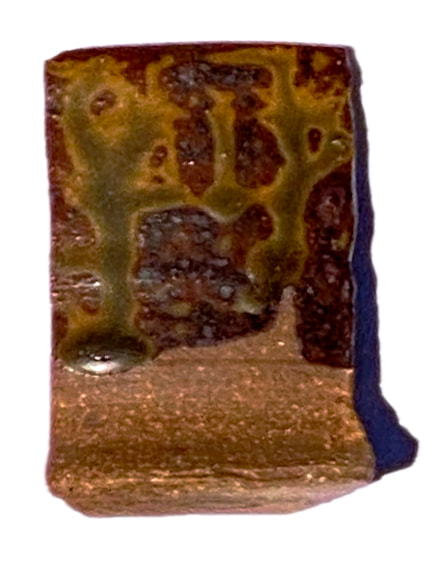
 Vase made from the new clay body featuring East 40 clay. You can see the clay with no glaze at the bottom, and where I did strokes of wax resist as seen on the view to the left. A glaze featuring the East 40 clay was used at the top of the pot, you can see it's darker than the glaze below the neck of the pot.. As promised, some results from the test kiln firing. After making the part 1 post, I realized that it was just too technical for a blog post. I reached a kind of crossroads where I realized I needed to create a section of the website for technical information. If you want something more in depth than this post, go to my new Ceramics-Technical page, and the pages that branch off of it. The little test kiln did reach cone 10 (approx. 2,381 F) but not without a battle of many hours in the sweltering heat. Luckily, it was worth it. The firing gave us really critical information; how will the new clay body behave at high-fire temperature in reduction (oxygen starved) kiln atmosphere, which is how we fire the wood kiln? And, how will the 25 glaze recipe variations with the East 40 clay look and behave on the new clay body? Overall, the results were a smashing success. Both clay body, glazes, and the way the glazes look on the clay body passed with flying colors. Again, I'm not going to go into all the technical results here, but I do want to show you some of the highlights of what came out of the little kiln. In the test bars above, you can see the color of the clay with no glaze for yourself. In addition to the tile in the test kiln firing, the dark one at the bottom of the photo, Gabbry Gentile was kind enough to fire the one on top in the electric kiln up at the ceramics studio in Penn Hall on the main campus. I formulated this clay body for high temperature firings like we do in the wood kiln at the East 40; the real shocker, was that this clay body works at the medium range temperature used in the studio on campus! I won't go into the technical details here, but suffice it to say I was honestly shocked at how well this clay performed in an electric kiln at mid-range temperature! Ash glazes are supposed to show dramatic drips; the trick is, you don't want them to run off the pot. This test tile was photographed on its back because of sun glare, but it was standing up on vertical when fired in the kiln. The pleasant surprise was that all the variations of the ash glaze stayed up on the tile, none of them ran off the tile at the bottom which is a big problem with a lot of ash glazes. Many ash glazes can only be used at the top of the pot, they are so runny. This was the runniest variation, and even it didn't run off the tile. Long story short, we already have usable glazes based on the East 40 clay and wood ash, and they work great on the new clay body! Above is the simplest glaze recipe I tested-and my favorite result! The drips are less dramatic without the eggshell. It's such stable glaze that I can see using it on an entire pot, not just at the top for a drippy effect. The color comes primarily from whatever is in the East 40 clay, educated guess, a lot of iron.
Getting back to the vase at the top of this post, the dark part at the top is the same as the tile above, except there is an addition of copper oxide. The pot was first dipped in a glaze we had on hand from previous wood kiln firings, we wanted to see how it worked on the new clay body. The red you see, especially on the view to the right is actually from the copper-rich glaze I was testing at the top! All in all, we got lots of very helpful information from the test kiln firing. In all honesty, I didn't expect this much success in a first time at full-temperature firing!
0 Comments
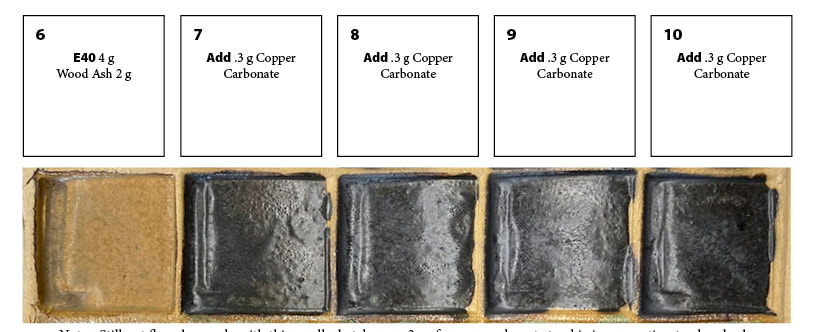
This summer I am working to formulate glazes and a clay body from the local clay dug from the Northampton Community College (NCC) East 40. https://www.ncceast40.org I’m weird; for me, waiting for the next glaze test to come out of the kiln is like a kid trying to wait to unwrap a present. But while I’m waiting for the tests that will come out of the kiln on Thursday, I thought I’d make a post about the preliminary testing I’ve already done. Spoiler alert-I’m going to show you the best first, see above. To set this up, you have to realize that the clay at the East 40 is very rich with ingredients (probably iron, maybe manganese) that go very dark when fired to the high temperatures (roughly 2,380 degrees) we use for our glaze firings. I discovered a “magic powder” from my kitchen, that makes the East 40 clay fire light, and opens up striking color possibilities! I get eggs from a local farm, and if you’re familiar with truly free-range eggshells, you realize they are at least twice maybe three times as thick as factory farm eggshells. That's why eggshells build up fast at my house! Eggshells are on average 95% calcium carbonate, and calcium carbonate is one of the most common and useful ceramic ingredients. In glazes, calcium carbonate is usually sourced from whiting or talc. Eggshells, when fired, shrink in volume tremendously, which can cause problems in glazes. I did a preliminary bisque firing of my ground up eggshells, so that the shrinkage would happen BEFORE I put them in a glaze. You can see on the left in the line blend above, how dark the East 40 clay fires even though tis test was fired at a lower temperature than we use in the gas and wood kiln firings at the East 40. But wait! Add a little eggshell, (second from left square) and the color changes. Add a little more (center) and wow, a totally different glaze color, without adding any colorant!! But wait, there’s more. Add a little black copper oxide (colorant) and you get one green, a tiny bit more and you get a different green! I designed an entire 25 section biaxial tile-5 rows of squares by 5 rows of squares-investigating the interaction between 4 ingredients, as inspired by this line blend. All of the variations use the East 40 clay, and wood ash which is used as a flux (an ingredient to melt the clay into a shiny glaze). The balance of East 40 clay to wood ash is varied, explored both with and without the other two ingredients, the eggshells and the black copper oxide. Look for a post on when this tile comes out of the kiln!  Like the tile above, this was the last row of a 25 section tile. Note that on the left, there is not enough wood ash to melt the clay enough to make a smooth and shiny glaze. Moving to the right, I'm adding a little more wood ash in each square. by tile 25 it loses the rocky texture of the first tile, getting closer to a usable glaze. Adding Wood Ash to East 40 Clay This test uses only two ingredients. Going left to right, I added increments of more wood ash to the East 40 clay. A few notes about this; for the ceramic artists out there, this was cone 6 oxidation. It's obvious that the 5 parts clay to one part ash is not nearly enough ash. (The ash is used as a flux, that is, to help melt the clay into a glaze.) I made impressions into each square with a finger, making a kind of "lake" within each square, and also applied the glaze unevenly to see how various thicknesses of the glaze would work. I'm working with such tiny amounts here that of course more testing is needed to nail down percentages, but it's pretty clear that the wood ash I was using, which was from the wood kiln at the East 40, needs to be over half the mix to melt the clay. I'm currently working on glazes for cone 10, so at that hotter temperature obviously everything will melt more than at this cone 6 (lower temperature) test. Adding a colorant I wish I had done the line blend of just the clay and wood ash first! Here there isn't enough wood ash in the mix to start, and as you add a colorant like copper carbonate, that tends to retard melting and make matters worse. Note that even .3 grams is way too much colorant for a first step! Instead of green, which we would expect from copper carbonate, we're almost at black. That's why I start with simple line blends-I'm not using much in materials to get this kind of information that points me in the directions I should go. Above, I used 4 g of East 40 clay to 2 parts of a commercially produced flux, the same percentage of clay to wood ash from the last test. The commercial flux has a stronger action but even so, it's under-melted. I'm using a commercial mason stain for the colorant. The main problem is that the clay when properly melted into a glaze is so inherently dark, it's hard to notice much color difference from the base glaze at left with no colorant. In the basic mix at left before I started adding rutile, it's melting ok but not great. Rutile can add color, texture and odd what I'll just call variations to the look of a glaze. Like the cobalt carbonate, it also makes the glaze more matte, or under-melted, under vitrified in ceramic terminology. Matte glazes are a thing, we don't always want super glossy glazes, but they can be more prone to leaching and other defects/weaknesses. I do want to do more tests with rutile going forward, just that every time I add an increment of rutile I know I need to add an increment of flux (melter) at the same time.
The way-back story I first used this clay when I was working on my master’s thesis, using a simple mix of half East 40 clay and half of a commercially available clay to make loom weights. (See crossing in my portfolio section) In my summer of 2022 Residency at the East 40, I used the clay, raw and roasted in a bonfire, as pigments for paints that I made and used in the “Imaginary Landscape” series of paintings that were featured in my Fall 2022 solo exhibition. During the residency, Walter Heath saw me grinding up rocks for pigments, and immediately had visions of using them to develop glazes. That summer I wasn’t ready to go there-but in 2023 I began preliminary testing, not just for the East 40 clay, but from local rocks I had picked up and processed. In this post I’m only showing the initial line blends I did with the East 40 clay, omitting all the rock glaze tests and tests on clay I dug out of my front yard-it’s a long enough post as is! |
Cindy VojnovicArtist & Educator Archives
September 2025
Categories
All
|
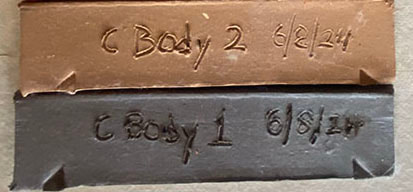





 RSS Feed
RSS Feed